I thought something was wrong when I saw my CPU speed going up and down. Later, I learned it’s normal for CPUs to adjust speed based on tasks to save power.
Is It Normal For CPU Clock Speed To Fluctuate? (Short answer)
Yes, it’s normal for CPU clock speed to fluctuate. Modern CPUs adjust their speed based on workload to optimize performance and energy efficiency. This helps manage power usage and heat.
In this article, we will discuss whether it is normal for CPU clock speed to fluctuate.
Understanding CPU Clock Speed Fluctuation
CPU clock speed fluctuation is how your processor changes its speed depending on your actions. When running heavy tasks, the CPU speeds up to handle the load. For lighter tasks, it slows down to save power and reduce heat. This helps the CPU work efficiently and extend its life. It’s a normal behavior designed to balance performance and energy use.
1. Thermal Throttling
Thermal throttling happens when your CPU or GPU gets too hot. To avoid damage, it slows down to cool off. This reduces performance but prevents overheating. Good cooling and airflow can help stop thermal throttling from happening.
Common Thermal Throttling Indicators and Solutions
Common Thermal Throttling Indicators:
- High CPU Temperature: Thermal throttling might start if your CPU exceeds 80°C during demanding tasks.
- Decreased Performance: You may notice slower speeds or lag when performing heavy tasks.
Solutions:
- Ensure Proper Cooling: Clean dust from fans and heatsinks regularly.
- Upgrade Cooling Systems: Consider improving your cooling setup, like adding better fans or using liquid cooling.
2. Power Management
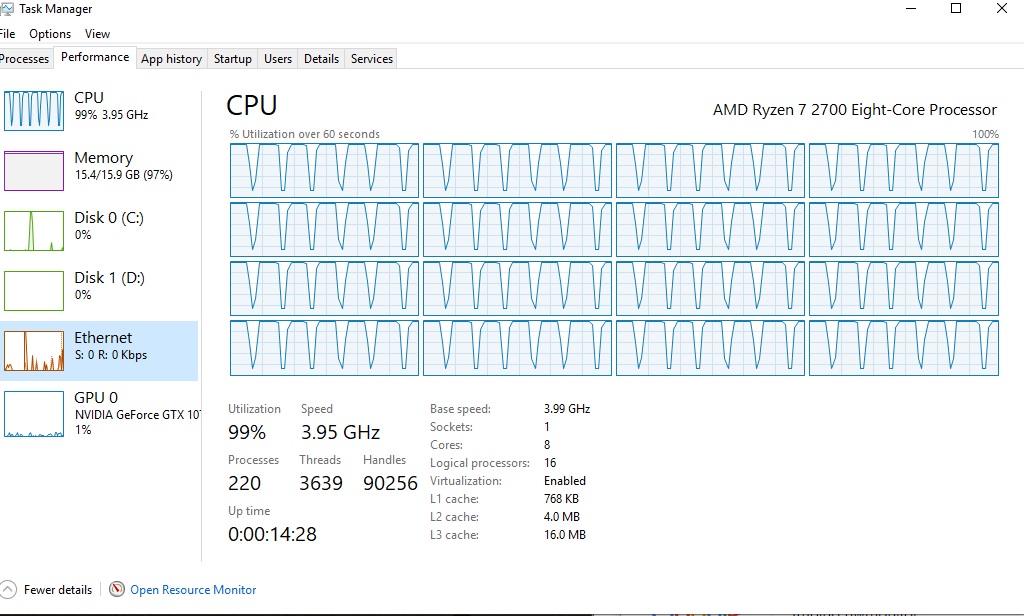
Modern CPUs use technologies like Intel’s SpeedStep and AMD’s Cool’n’Quiet. These adjust clock speeds automatically to balance performance and power use, saving energy and lowering heat.
Tips for Managing Power Settings
- Adjust Power Settings: Balance performance and energy use in system settings.
- Enable High-Performance Mode: For heavy tasks, switch to high-performance mode.
- Customise Power Plans: Set power plans to match your specific needs.
3. Workload and Processor Demand
The CPU changes its clock speed based on the task. For demanding tasks, it speeds up to boost performance. For lighter tasks, it slows down to save power and reduce heat. This helps balance performance and energy efficiency.
Factors Affecting CPU Workload and Demand
Task Type: Intensive tasks like gaming or video editing need more CPU power, while simpler tasks like web browsing require less.
Number of Applications: Running multiple programs simultaneously increases CPU demand.
Software Efficiency: Well-optimised software uses CPU resources better than poorly optimized ones.
System Background Processes: Background tasks and services can add to CPU workload.
Hardware compatibility: Older or less powerful CPUs may struggle with modern, demanding applications.
4. Ageing and Degradation
As CPUs get older, they may run slower and show more speed changes. Continuous heat and use can wear them down, reducing performance. Keeping them cool and well-maintained can help slow down these effects.
Signs of CPU Aging and Degradation
Type of Applications: Demanding tasks, such as gaming or video editing, require higher clock speeds to perform well.
Simultaneous Applications: Using multiple programs at the same time influences how the CPU adjusts its speed.
CPU Core Utilisation: The number of active cores affects how the CPU’s clock speed fluctuates according to the workload.
5. Thermal Throttling and Power Management
Thermal Throttling: When the CPU gets too hot, it slows down to cool off and prevent damage. This can reduce performance but helps keep the hardware safe.
Power Management: Controls how the CPU uses energy. It adjusts speed to balance performance and save power, improving efficiency and battery life.
6. Voltage and Frequency Scaling
Voltage Scaling: Adjusts the amount of electrical power supplied to the CPU. Lowering voltage reduces power use and heat but can affect performance.
Frequency Scaling: Changes the CPU’s clock speed. Higher frequencies boost performance, while lower frequencies save energy and reduce heat. Both scaling methods help balance performance and efficiency.
7. Turbo Boost and Overclocking
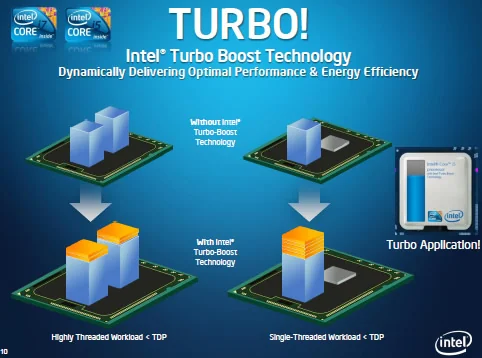
Turbo Boost: A feature in modern CPUs that automatically increases clock speed beyond the base level when extra power is needed, like during heavy tasks. It helps boost performance without manual adjustments.
Overclocking: Manually increasing the CPU’s clock speed beyond its default settings to improve performance. While it can enhance speed, it may cause overheating and shorten the CPU’s lifespan if not done carefully with proper cooling.
8. Operating System and Software Influence
The operating system (OS) and software can impact CPU performance. An efficient OS and well-designed programs use CPU power effectively. Poorly optimized software or an outdated OS can cause the CPU to work harder, slowing down performance.
9. Monitoring and Managing CPU Clock Speed Fluctuations
Monitoring: Use tools like HWMonitor or CPU-Z to track real-time clock speeds, temperatures, and performance metrics.
Managing:
- Improve cooling: Ensure good airflow and clean cooling systems.
- Adjust Power Settings: Optimise power plans for performance or energy savings.
- Update Drivers: Keep CPU and motherboard drivers current for stability.
Exploring Other Factors of CPU Clock Speed Fluctuation
1. Bios Settings and Firmware
BIOS Settings: The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) controls basic hardware functions. Settings here, like CPU speed and power options, can affect clock speed and performance.
Firmware: Firmware is software on hardware devices that manages their functions. Keeping it updated ensures stability and optimal performance.
2. Background Processes and Software
Background Processes: These are programs running behind the scenes. They can use CPU resources and affect clock speed by adding extra workload.
Software: Poorly optimized or outdated software can cause the CPU to work harder, leading to fluctuating speeds. Regular updates and efficient software help maintain stable performance.
3. Voltage and power supply instability
Voltage Instability: Fluctuations in the electrical voltage supplied to the CPU can cause irregular clock speeds. Consistent voltage is crucial for stable performance.
Power Supply Issues: A failing or inadequate power supply can lead to unstable CPU performance and speed changes. Ensuring a reliable and sufficient power source helps maintain consistent CPU operation.
Fluctuation of CPU Clock Speed
The CPU’s clock speed can change because of how hard it’s working, heat levels, power settings, and voltage stability. It speeds up for heavy tasks and slows down to save energy and prevent overheating.
Exploring Advanced Aspects of CPU Clock Speed Fluctuations
1. CPU Architecture and Generation
Architecture refers to the design and structure of the CPU, including how it processes data and instructions. Different architectures affect performance and efficiency.
Generation Indicates the age and advancements of a CPU model. Newer generations typically offer better performance, improved energy efficiency, and new features compared to older ones.
2. Multithreading and Clock Speed Distribution
Multithreading: Allows a CPU to handle multiple tasks or threads simultaneously. It can improve performance by dividing work across multiple cores or threads.
Clock Speed Distribution: In a multithreaded system, the CPU allocates clock speed across different threads or cores. This helps balance the workload and improves overall efficiency and performance.
3. Benchmarking and stress testing
Benchmarking: measures the performance of your CPU by running standardised tests. It helps compare your CPU’s speed and efficiency against other models or previous performance.
Stress Testing: Pushes the CPU to its limits to see how it performs under maximum load. It helps identify stability issues, overheating, and performance bottlenecks.
Reasons for Clock Speed Fluctuations
1. Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling
Dynamic Voltage Scaling: Adjusts the amount of electrical power supplied to the CPU based on current needs, helping to save energy and reduce heat.
Dynamic Frequency Scaling: Changes the CPU’s clock speed according to the workload. It increases speed for demanding tasks and lowers it during lighter use to balance performance and power consumption.
2. Thermal Throttling
Thermal throttling happens when a CPU gets too hot. To prevent overheating and damage, the CPU slows down its speed. This reduces performance temporarily but helps keep the hardware safe and extends its lifespan.
3. Power Limits and Turbo Boost
Power Limits: Set boundaries on how much power the CPU can use. This helps manage heat and energy consumption, ensuring the system stays within safe operating conditions.
Turbo Boost: Increases the CPU’s clock speed beyond its base level for short periods when extra performance is needed. This feature enhances speed during demanding tasks but relies on staying within the power and thermal limits.
4. Background processes
Background processes are programs running invisibly while you use your computer. They use CPU resources and can affect system performance. Managing or closing unnecessary background processes can help improve overall speed and efficiency.
Impact on Performance
1. Optimised Power Consumption
Optimized power consumption means using energy wisely to get the best performance while saving power. It involves settings like power-saving modes, adjusting screen brightness, and closing unused apps to extend battery life and cut energy use.
2. Performance on Demand
Performance on demand means adjusting your device’s speed and power based on current needs. It provides extra performance when required for heavy tasks and saves energy during lighter activities, balancing efficiency and power use.
3. System Stability
System stability refers to how reliably a computer or device operates without crashing or experiencing errors. A stable system runs smoothly, handles tasks consistently, and maintains performance without unexpected interruptions or failures.
Monitoring and Managing Clock Speed
1. Monitoring Tools
Monitoring tools are software or utilities that track and display system performance, including CPU usage, temperatures, and memory usage. They help you keep an eye on how well your device is running, identify issues, and optimize performance.
2. Cooling Solutions
Cooling solutions are methods or devices used to keep your computer or CPU cool and prevent overheating. These include fans, heatsinks, liquid cooling systems, and thermal paste. Effective cooling helps maintain performance and prolongs the lifespan of your hardware.
3. Bios/UEFI Settings
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) are firmware interfaces that manage hardware settings. In BIOS/UEFI, you can adjust settings for CPU performance, memory, and boot options to optimize your system’s operation and stability.
4. Software Management
Software management involves organizing, updating, and maintaining applications on your device. It includes installing updates, removing unused programs, and ensuring that software runs efficiently. Good software management helps improve system performance and security.
When to Be Concerned
1. Consistent Throttling Under Light Load
Consistent throttling under light load means that the CPU regularly slows down even during low-demand tasks. This can occur to save energy and reduce heat, but it may affect performance if it happens too frequently.
2. Unusual Performance Drops
Unusual performance drops refer to sudden or unexpected reductions in your device’s speed or responsiveness. These drops can be caused by issues such as overheating, software conflicts, or hardware problems, affecting overall efficiency and usability.
3. High idle temperatures
High idle temperatures refer to a situation where your computer’s CPU or other components run at unusually high temperatures even when the system is not actively doing heavy tasks. This can indicate cooling issues or hardware problems.
Is CPU Clock Fluctuation Normal at Idle?
Yes, CPU clock fluctuation at idle is normal. The CPU adjusts its clock speed to save power and reduce heat when it’s not under heavy load. This helps improve energy efficiency and prolongs the hardware’s lifespan.
Is It Normal For CPU Clock Speed To Fluctuate Windows?
Yes, it’s normal for CPU clock speed to fluctuate in Windows. The operating system and power management features adjust the CPU’s speed based on the current workload to balance performance and energy efficiency. This helps manage heat and power consumption effectively.
CPU Clock Speed Jumping While Idle
It’s unusual but can happen. If the CPU clock speed fluctuates significantly while idle, it may be due to background processes, power management settings, or thermal issues. Checking for background tasks and ensuring proper cooling can help stabilize the idle clock speed.
CPU Idle Clock Is Fluctuating So Much
If your CPU’s idle clock speed is fluctuating significantly, it might be due to background processes using CPU resources, aggressive power management settings, or thermal issues. To address this, try:
- Checking background processes: Ensure no unnecessary programs are running.
- Adjusting Power Settings: Set your power plan to balanced or power saver mode.
- Improving Cooling: Ensure your system is properly ventilated and clean.
CPU Clock Heavily Fluctuating While PC Is Idle, Is This Normal?
It’s unusual for the CPU to fluctuate a lot when idle. Some changes are normal, but big swings may mean background tasks are active, power settings are too aggressive, or cooling is needed. Check these factors to stabilize the clock.
CPU Insane Clock Speed Fluctuation – Is This Normal?
Extreme clock speed changes are not typical. While some fluctuation is normal, huge swings may signal issues like background tasks, aggressive power settings, or cooling problems. Check for unnecessary programs, adjust power settings, and ensure good cooling.
CPU Clock Speed Fluctuating B/W 1.5 To 3.6 Mhz, Mostly Stuck At 1.5 Mhz
If your CPU speed mostly stays at 1.5GHz but sometimes goes up to 3.6GHz, it could be due to power-saving settings, overheating, or background programs. Check settings, cooling, and running apps.
Are frequently fluctuating clock speeds normal?
Yes, it’s normal for clock speeds to fluctuate frequently. The CPU adjusts its speed based on the workload to balance performance and power use. This helps manage heat and save energy during different tasks.
Should CPU clock speed fluctuate like this?
A certain amount of fluctuation in CPU clock speed is normal, as the CPU adjusts its speed based on workload. However, if the fluctuations are extreme or constant, it may indicate issues such as power management settings, thermal problems, or background processes.
Why Does My CPU Clock Speed Fluctuate Up and Down Running Intelburntest?
If your CPU clock speed fluctuates up and down while running IntelBurnTest, it could be due to:
- Thermal Throttling: The CPU slows down to prevent overheating if temperatures rise too high.
- Power Management Settings: Settings might be adjusting the clock speed to balance performance and power consumption.
- Boost Technology: The CPU might be using Turbo Boost to temporarily increase speed but adjust as needed based on thermal and power limits.
- System Stability: The test might stress the CPU, causing fluctuations to maintain stability and prevent damage.
Ensure your cooling system is adequate and check power management settings to help stabilize clock speeds.
Is It Normal For My CPU Multiplier and Speed To Be Changing That Much On Idle? (I7 – 9700k)
Yes, it’s normal for your Intel i7-9700K CPU multiplier and speed to change a lot while idle. The CPU adjusts its speed to save power and reduce heat when not working hard. Extreme changes might need checking.
Is It Normal For My CPU to Run at High Ghz All The Time?
No, it’s not typical for the CPU to run at high GHz all the time. CPUs usually adjust their speed based on workload to save power and reduce heat. If your CPU is always at high speeds, it may indicate a problem or need for adjustment.
My CPU Speed Is Fluctuating A Lot
If your CPU speed is fluctuating a lot, it might be due to:
- Power Management: The CPU adjusts speed based on workload to save energy.
- Thermal Throttling: The CPU slows down to prevent overheating.
- Background processes: Other programs might be using CPU resources.
- System Settings: Power and performance settings could be influencing speed.
Check these factors to understand and stabilize the fluctuations.
CPU Speed Fluctuates Or Appears Slower Than Expected
If your CPU speed fluctuates or seems slower than expected, it might be due to overheating, power-saving settings, background tasks, or system issues. Check cooling, adjust power settings, and close unnecessary programs to improve performance.
CPU clock speed jumping while idle
If your CPU speed jumps while idle, it’s usually because of power-saving features, background apps, or cooling adjustments. To stabilize it, close unused programs, adjust power settings, and ensure good cooling.
FAQ,s
1. Is CPU Clock Speed Supposed to Fluctuate?
Yes, CPU clock speed is supposed to fluctuate. It adjusts based on workload to balance performance and energy use.
2. Why Does My CPU Clock Speed Keep Changing?
Your CPU clock speed changes to adjust performance and save energy based on what tasks you’re doing and how hot it gets.
3. Is It Normal For CPU Usage To Fluctuate?
Yes, it’s normal for CPU usage to fluctuate. It changes based on what tasks or programs are running at any given time.
4. How To Stop CPU Speed From Fluctuating?
To reduce CPU speed fluctuations:
- Adjust Power Settings: Set your power plan to “High Performance.”
- Improve cooling: Ensure good airflow and clean cooling systems.
- Close unnecessary programs: reduce background tasks.
- Update Drivers: Keep your system’s drivers and BIOS up to date.
These steps help stabilize the CPU’s performance.
5. Is It Normal For CPU Clock Speed To Fluctuate Windows?
Yes, it’s normal for CPU clock speed to fluctuate in Windows. The CPU adjusts its speed based on the current workload to balance performance and energy use.
6. Is It Normal For GPU Clock Speed To Fluctuate?
Yes, it’s normal for GPU clock speed to fluctuate. The GPU adjusts its speed based on workload to balance performance and energy use, increasing during heavy tasks and decreasing when not needed.
7. Is It Normal If CPU Keeps Jumping From 1400 To 3500 Mhz, etc?
Yes, it’s normal for a CPU to jump between speeds like 1400 MHz and 3500 MHz. The CPU adjusts its speed based on how much work it’s doing. It speeds up for heavy tasks and slows down to save energy when idle.
8. Are frequently fluctuating clock speeds normal?
Yes, it’s normal for clock speeds to change often. Your processor adjusts its speed based on tasks to save power and manage heat. High-demand tasks need more speed, while low-demand tasks use less.
9. CPU Clock Speed Fluctuating?
Yes, it’s common for CPU clock speeds to go up and down. The CPU adjusts its speed depending on the task faster for heavy work like gaming or video editing and slower for light tasks like web browsing to save energy.
Conclusion
Yes, it’s normal for CPU clock speed to fluctuate. This happens as the CPU adjusts its speed based on workload to balance performance and energy use. Minor fluctuations are typical, but significant changes might signal issues like overheating, power settings, or background tasks.



